FACTORY AUTOMATION &
INSTRUMENTATION CORP.

AOP WATER TREATMENT SOLUTION
COMPACT SYSTEMS FOR WATER AND WASTEWATER TREATMENT
Advanced chemical oxidation processes make use of oxidants to reduce COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) and BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand) levels, and to remove both organic and oxidizable inorganic components.
-
The processes can completely oxidize organic materials to carbon dioxide and water.
-
There is a wide variety of advanced oxidation processes.
-
Chemical oxidation process using ozone generated from the air from the atmosphere.
-
Advanced Oxidation Processes are particularly appropriate for effluents containing refractory, toxic or non-biodegradable materials.
The processes offer several advantages over biological or physical processes, including:
-
Process operability (No biological process)
-
Unattended operation with very small foot print.
-
The absence of secondary wastes (sludge).
-
The ability to handle fluctuating flow rates and compositions.
The COD level output after conventional waste water treatment is usually not low enough, and further steps are necessary or additional treatment or process are needed in order to reduce the excess of COD contamination.
Chemicals like aromatic rings, phenols, chlorinated carbohydrates, lipids and certain proteins are usually not affected by the biological process.
Conventional oxidation processes reduces COD level by aerobic and anaerobic biological digestion. Some of the compounds that create COD in the waste water are not responding to the biological treatment as a result of their chemical nature, some of them are toxic to the digesting micro-organisms, and others need more effective oxidation process in order to be removed from the wastewater.
Technology application intended for all type of waste water sources, utilizing the ozonation, electro-winning cell and mechanical filtration technique for a simple, compact modular design, with short retention time for high volume flow rate and yet very effective and economical mode of treatment.
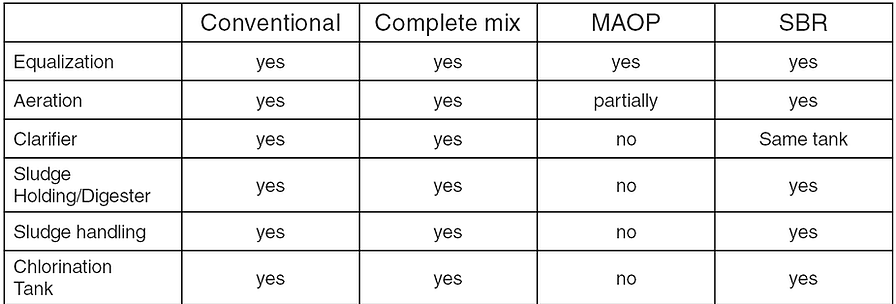
Comparison of Technologies - Process Components
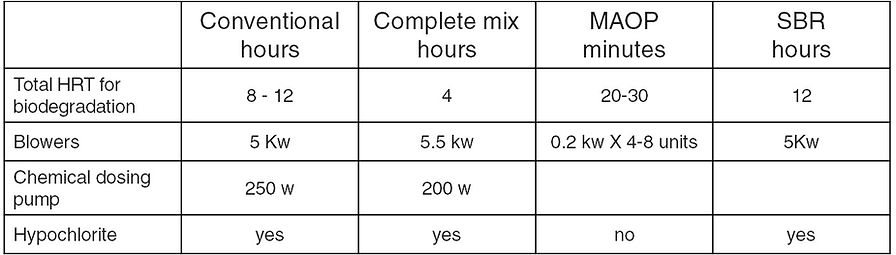
Comparison of Technologies - Typical Processes HRT